After a year of having sexual relations without achieving an evolutionary pregnancy, it is suspected that there may be some fertility problem, either in the man, in the woman, or in both. In order to find it out, it is necessary to make a series of tests for both members of the couple.
Specifically, the most frequent tests to assess fertility in men are the seminogram, physical examination and hormonal analysis. In addition to these basic studies of male fertility, there are other more specific tests such as the hypoosmotic test, sperm FISH, karyotype, etc.
In this article, we will talk about all these tests that men undergo who want to become parents and do not succeed naturally.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 4.6.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Physical Exam
One of the first steps in case of suspicion of male infertility is to make an anamnesis of the patient. It consists of an interview with the specialist in order to analyse the general health of the patient, his medical history, the quality of sexual relations, etc.
The male reproductive system is then analyzed to study the presence of any physical abnormality that may be impeding conception.
Usually, the specialist (urologist) performs the following:
- Male Height and Weight
- Abdominal, groin, penis, testicles and prostate exams and palpation. In the case of the testicles, aspects such as their volume or consistency will be carefully studied.
- Ultrasound of the genital area (not always done)
With this scan, the aim is to discover if there is any problem in the genital anatomy that complicates the deposition of semen in the vagina. In addition, testicular palpation may lead the specialist to suspect an error in spermatogenesis (production of spermatozoa) or some alteration that prevents the spermatozoa from leaving when ejaculating.
In any case, in order to confirm the last one, it will be necessary to carry out other tests such as those described below.
Seminogram
After checking that there are no anatomical problems that hinder intercourse, a seminogram, also known as a spermiogram or spermogram, is performed.
This is a detailed analysis of a semen sample obtained by masturbation after a period of abstinence of between 3 and 5 days. In this sperm examination, we analyze the sample, both with the naked eye and under the microscope. We study different parameters of seminal quality, which allows us to estimate the fertilization capacity of the spermatozoa.
These are the most common aspects that are analyzed:
- Volume of ejaculated semen
- Viscosity
- pH
- Sperm Motility
- Morphology
- Sperm concentration
- Presence of foreign cells
- Vitality
Based on the results obtained and their comparison with the reference values established by the WHO, the quality of the semen analyzed will be determined.
If an anomaly is detected, the corresponding pathology should be diagnosed. The most common are:
- Azoospermia: when there are no spermatozoa in the analyzed ejaculate.
- Asthenospermia or asthenozoospermia: when the sperm present motility problems.
- Oligospermia or oligozoospermia: when the sperm concentration is low (less than 15 million spermatozoa/ml).
- Teratospermia or teratozoospermia: when more than 96% of the spermatozoa have an abnormal morphology.
Assisted procreation, as any other medical treatment, requires that you rely on the professionalism of the doctors and staff of the clinic you choose. Obviously, each clinic is different.
If you want to know more about this exam, you should read this post: What Is a Semen Analysis Report? – Purpose, Preparation & Cost.
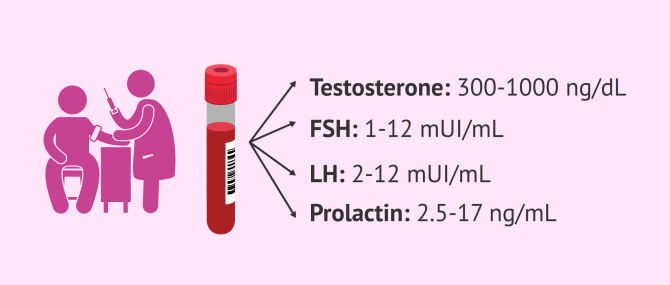
Male Hormones Analysis
The production of sperm takes place in the testicle thanks to the action of sexual hormones. An alteration of the hormonal system can make spermatogenesis difficult or impede it and, as a result, lead to low seminal quality and male infertility.
Below are the most commonly analyzed hormones in men.
- Testosterone
- normal adult testosterone values are between 300 and 1,000 ng/dl. When a man has lower than normal levels, it may indicate delayed puberty, benign pituitary tumor, testicular trauma, infection, immune disorders, etc. On the other hand, if the male contains high levels of this hormone it is related to testicular cancer, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, androgen resistance, consumption of specific drugs or medicines, etc.
- FSH
- also known as follicle-stimulating hormone. It is a hormone that is synthesized by the pituitary gland and whose normal values are between 1 and 12 mIU/mL. The FSH hormone stimulates the action of Sertoli cells, which promotes testosterone synthesis and sperm production.
- LH
- also known as luteinizing hormone. It is a hormone that is synthesized by the pituitary gland and whose normal values are between 2 and 12 mIU/mL. The LH hormone stimulates the action of Leydig cells, related to testosterone production.
- Prolactin
- is a hormone related to the activity of the LH hormone and the synthesis of testosterone. Its normal values should be between 2.5 and 17 ng/mL. Higher values of prolactin hormone than indicated are associated with low testosterone levels, male impotence, gynecomastia, infertility, hypothyroidism and suspected pituitary tumor.
Additional tests
Semen analysis, the exploration of the genitals, and the analysis of hormones are the basic tests that are carried out to determine the state of the man's fertility and to try to discover the causes for which the pregnancy has not been achieved.
When these tests do not help to diagnose the reason for infertility or when the diagnosis obtained needs to be confirmed, additional tests can be requested such as those discussed in the following sections.
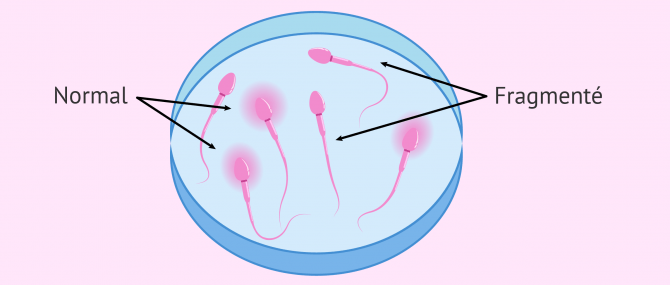
DNA Fragmentation Study
One of the fragmentation tests consists of identifying the presence of spermatozoa with halo (normal) from those without halo (fragmented). By placing the sperm in an acidic medium, the structure of the DNA strand is broken and a halo appears around the head of the spermatozoa. If the DNA strand is fragmented, the acidic medium does not cause the strand to unwind and therefore we do not observe the halo.
Men who show more than 30% fragmentation of sperm DNA will need to use assisted reproductive techniques to achieve pregnancy.
Karyotyping
Karyotyping is the study of the set of chromosomes in a cell. This cytogenetic test allows the discovery of genetic abnormalities that may be the cause of infertility. To do this, it is simply necessary to take a blood sample.
Nowadays, karyotyping has become a routine test in most fertility centers.
Semen Culture
Also known as sperm culture, this is a bacteriological study. It is usually requested when, in the seminogram, a concentration of leukocytes greater than 1 million/ml of semen is observed. This is usually indicative of infection and, therefore, culture is very useful, as it can help us to determine which is the infectious agent.
Testicular pain, inflammation of the testicles, blood in the sperm, or any change in color or smell in the semen are also indications of seminal culture.
Testicular Biopsy
It consists of extracting, by surgery, a small fraction of the testicle, and then analyzing it in the laboratory in search of viable sperm. Indeed, sperm are obtained directly from the testicle.
This test is useful in cases of azoospermia, as it permits to distinguish whether it is a problem of sperm production (secretory azoospermia) or blocking the passage of the same (obstructive azoospermia).
On the other hand, in addition to a diagnostic test, it is also a treatment to achieve pregnancy because in the event of viable sperm is found, it allows the ICSI technique (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) to be carried out.
If you are interested in this technique, we recommend you read the following post: What Is a Testicular Biopsy? – Purpose & Procedure.
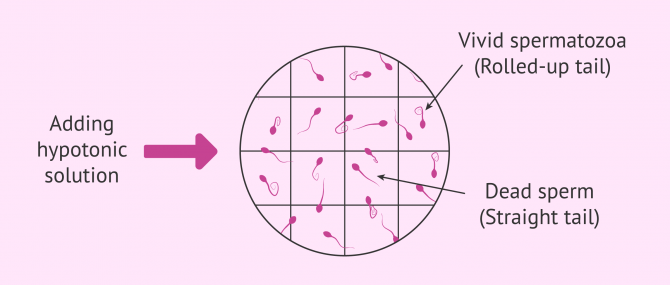
Hypo-osmotic Test
In order for the sperm to penetrate the egg and allow fertilization, it is necessary that its membrane is undamaged and functions correctly. To check this, we can perform the hypo-osmotic test.
It consists of introducing the spermatozoa into a low salt medium (hypotonic medium), so that, if the membrane is intact, the medium will pass into the spermatozoa by osmolarity and it will swell in the tail.
Sperm FISH
Another very common test in men is the fluorescent in situ hybridization or FISH of sperm, a cytogenetic test that marks certain chromosomes in the sperm with fluorescent probes. In this way, it is possible to determine whether the spermatozoa contain the normal chromosomal endowment, as they would only have one fluorescent signal for each chromosome analyzed.
Spermatozoon FISH is recommended when there are alterations in the karyotype, seminograms with abnormal values, after oncological treatment, implantation failures in previous cycles, etc.
FAQs from users
Which values are considered normal in a semen analysis report?
Concentration > 15million/ml
Motility > 40%
Morphology > 4%
Vol > 1.5ml
Are there any symptoms that might indicate whether or not I am a sterile man?
Generally, most male fertility disorders do not result in specific symptoms. However, there are some of them that can lead to inflammation and redness of the genital area, changes in the color, smell or texture of semen, pain, etc..
For example, a man may have no symptoms of azoospermia and only discover this seminal pathology by performing the seminogram. On the contrary, a hormonal imbalance can give rise, for example, to mood swings, loss of libido or other symptoms that mean that there may be a problem.
Are there any male fertility tests that can be done at home?
There are home tests that can be purchased at the pharmacy and that allow you to measure some parameters of semen quality such as concentration. Many people know them as male predictors.
However, these fertility tests measure only one or two seminal parameters and are not very reliable. That is why it is always recommended to carry out the complete seminogram in a specialised centre.
Suggested for you
In this post, we mentioned the main seminal alterations that can be discovered through the sperm analysis. If you want to learn more about sperm quality, please read our article: Semen Quality: What Is Measured And What Can Be Done To Improve It?
On the other hand, we have commented that infertility may be due to problems in the man, the woman, or both. For this reason, if there is no pregnancy after one year, not only the man but also the woman should be tested. Learn about the most common female fertility tests in this article: Female Fertility Testing: How Does it Work?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Authors and contributors









I recently got my semen analysis results. Could you help me interpret these?
volume:1 ml
aspect : opalecent grey
ph:7.0
viscocity :increased
liquefaction: 40 minutes
PARAMETER:
CONCENTRATION. 18.5 MILLION/ML
TOTAL CONCENTRATION :18.5 MILLION
MOTILITY :PROGRESSIVE :33.8 %.
NON-PROGRESSIVE: 60.5%.
IMMOTILE: 5.7 %.
NUMBER OF MOTILE SPERM: 6.2 MILLION
MOTILITY:95.4
MORPHOLOGY
NORMAL:35.8%
ABNORMAL:64.2%
HEAD DEFECT:53.2%
PART DEFECT:9.7
SCOURGE DEFECT:0.5%
CYTOPLASMIC RESIDUE :0.8%