From the time of in vitro fertilization until the embryos are transferred to the female uterus, embryonic development occurs in the laboratory in what is known as 'in vitro' embryo culture.
In this article we will talk about the development of IVF embryos when they are in culture, that is, outside the woman's body.
Provided below is an index with the 6 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 1.2.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Embryonic Development
Regardless of whether in vitro fertilization (IVF) is done conventionally or through microinjection (ICSI), between 16 and 20 hours after the union of egg and sperm, it is checked whether fertilization has taken place or not. At this time we must distinguish 2 polar bodies (PB) in the periphery and 2 pronuclei (PN) in the center of the embryo. If we do not observe this structure, we confirm that fertilization has not occurred or has occurred abnormally. Therefore, embryos that do not present 2PB and 2PN during fertilization observation will be discarded, i.e. they will not be kept in culture.
Next, the pronuclei, which correspond to the maternal and paternal nuclei respectively, merge and give rise to the so-called zygote which is the first embryonic stage (day 1 post-fertilization). This is a cell with one single nucleus only.
Subsequently, the zygote initiates the successive divisions that will allow the evolution of the embryo. Thus, the different stages of embryonic development take place:
- On day 2
- 2-4 cell embryo.
- On day 3
- embryo of about 8 cells.
- On day 4
- embryo in the so-called morula stage, with approximately 16-32 grouped cells that begin to compact.
- On day 5
- embryo with about 100 cells totally compacted and impossible to distinguish.
- On day 6
- blastocyst stage embryo, with two differentiated cell types.
These are the different stages of embryonic development:
From zygote to morula
Once the maternal and paternal NPs have fused and therefore the zygote has been obtained, the embryo continues its development. Thus, the successive divisions begin throughout the first days of culture.
From each cell or blastomere we will obtain two new cells. In this way, on day 2, the embryos have between 2 and 4 cells and on day 3 the 8 cells are around.
Four days after fertilization, the embryo is in the morula stage: it has about 16-32 cells and cell compaction begins. The beginning of the compaction does not distinguish very well the cells and the embryo has the appearance of blackberry, hence its name.
Blastulation: formation of the blastocyst
On day 5, the embryo has approximately 100 cells, although totally compacted and impossible to distinguish. At this point of development begins what we know as blastulation, which consists of:
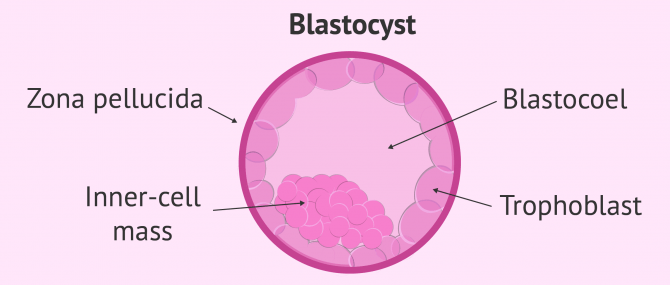
- Formation of a fluid-filled internal cavity called a blastocoel.
- Differentiation of cells into two cell types: trophectoderm (or trophoblast) and inner cell mass (ICM).
At this time of development, the embryo is called a blastocyst.
Around day 6 of embryonic development, the expansion of the embryo takes place. Contractions begin and the zona pellucida (the layer that surrounds the embryo) begins to thin until hatching occurs, that is, the exit of the inner cell mass (ICM) and trofoectoderm.
This allows the embryo to leave the zona pellucida to adhere to the endometrium and implant into the uterine cavity, which marks the beginning of pregnancy.
Embryo culture in the IVF laboratory
As we have mentioned, after fertilizing the egg in the laboratory, the embryos obtained are left in culture so that they can begin their development until the day of the transfer or, failing that, until the day they are to be vitrified (frozen) for use in further treatments.
In order to allow proper development in the in vitro fertilization laboratory, it is essential to mimic the environmental conditions in which embryos grow naturally, i.e. the conditions of the female reproductive system:
- Temperature around 37ºC
- Relative humidity close to 95%
- Low concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide (5-7%). A 21% O2 concentration also allows for good embryo growth.
- Air purity
- Light (work should be done with as little light as possible)
Any alteration of the environment or variation in the culture medium where the embryos grow in vitro can block their proper development. It is therefore essential that the environmental conditions of the IVF laboratory be carefully studied and monitored.
Embryo transfer
The embryos can be cultured until day 3 or day 5, depending on when the transfer or cryopreservation is to be carried out.
The decision of the time of culture (until day 3 or day 5) is made by the medical team depending on each situation. Factors such as the number of oocytes fertilized, the quality of the embryos, the endometrial preparation, the need or not for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), etc., are taken into account.
In relation to the quality of the embryos, aspects such as the rhythm of division or their morphology are analysed.
FAQs from users
When does embryonic development end and fetal development begin?
The embryo is called a fetus from the eighth week of development. Therefore, from now on, we can talk about fetal development and not embryonic development.
Is embryonic development studied day by day or week by week?
In cases of IVF, it does not make much sense to talk about embryonic development for weeks, since embryo culture does not extend beyond day 6-7. In fact, embryos are usually transferred or cryopreserved before one week of evolution.
Once inside the maternal uterus, we can already speak of embryonic development for weeks. In any case, as we have indicated in the previous question, embryonic development lasts until week 8. Therefore, from then on we will coin the term fetal instead of embryonic.
What are the main stages of early human embryonic development?
As we have explained throughout the article, there are several key stages during the growth of the embryo until its implantation. First, immediately after fertilization, we find the zygote (a single cell that results from the union of the genetic endowment of the egg with that of the sperm).
The embryo is then divided into 2 cells, then into 4, then into 8... and so on until the so-called morula is formed (day 4). This is a grouping of about 32 cells that begin to compact and, therefore, we do not clearly appreciate their limits.
This conglomerate of cells will compact completely and give rise to the blastocyst, in which we distinguish three clear parts: the cells of the trophectoderm or trophoblast, the cells of the inner-cell mass and the blastocoel or central cavity.
Is it correct to speak of embryonic development until the ninth month?
It is not totally correct, because from week 8 of embryonic evolution, the embryo becomes called a fetus and, therefore, it is more correct to speak of fetal development from week 8 of gestation until birth.
Suggested for you
Embryonic culture takes place in IVF process. If you want to learn more about all the IVF process in surrogacy, we recommend you to read this post: What Is IVF Surrogacy? – Process, Success Rates & Cost.
Moreover, if you need more informations about surrogacy process, you should read this article: What Is Surrogacy & How Does It Work? – Everything You Should Know
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Author